Processing Conditions of Samples
Materials
Fiber reinforced composites are composed of 2 componenent: the matrix and the fiber. Our sample matrix is composed of polypropylene melt. The density of the polypropylene in these samples is 9.4 g/cm3. General properties for polypropylene can be found here. The fiber component is glass fiber with a density of 2.54 g/cm3.
Processing
Creation of the fiber reienforced composite samples consists of two steps: hot melt impregnation and extrusion/compression molding.
Hot melt impregnation
Hot melt impregnation is a processing method used with thermoplastic materials to adequately wet the reinforcement with the matrix polymer. The following image illustrates the melt impregnation process.
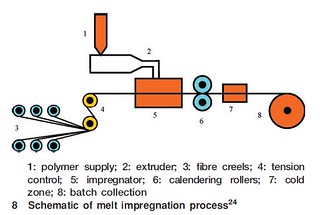
Adequate wetting is important to final product properties because it ensures the bond between the fiber and the matrix. In hot melt imprgnation, fiber is pulled from a roll and heated above the melting temperature of the chosen polymer. For the polypropylene used to make these samples processing temperatures would be in excess of 174 degrees Celcius. Simultaneously, the polymer resin will be compounded through an extruder. The heated fiber bundels are then spread apart and the hot polymer is added. Finally the combined fiber/polymer compound is pulled through an extruder and cooled. After impregnation, the coated fibers are chopped to form Long Fibre Thermopostics(LFT) pellets of length approximately 12.7 mm (0.5 inch). The pellets are then used for extrusion/compression molding.
Extrusion/Compression Molding
After impregnation, the pellets are then placed into an extruder and extruded into a compression molding apparatus. This isllustration shows the
typical setup for an compression molding machine.
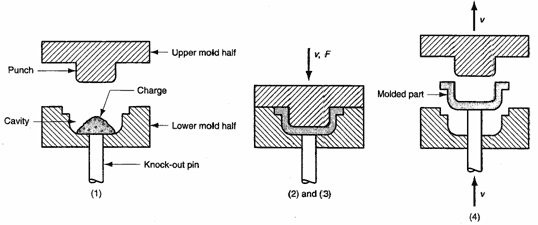
Image source: http://www.sinotech.com/images/compressionTransfer2.gif
The process pictured above differs somewhat from our process in that for our process the material is inserted by extrusion for increased consistancy between parts. Extruding the material into the mold allows for knowledge of the direction of flow of the material and provides uniformity. Heat and pressure are applied to the material to mold the material into the final shape. The compression molding has several distict advantages including that parts molded in this fashon show less breakage of fibers which is important for this application.